APIs
Authentication
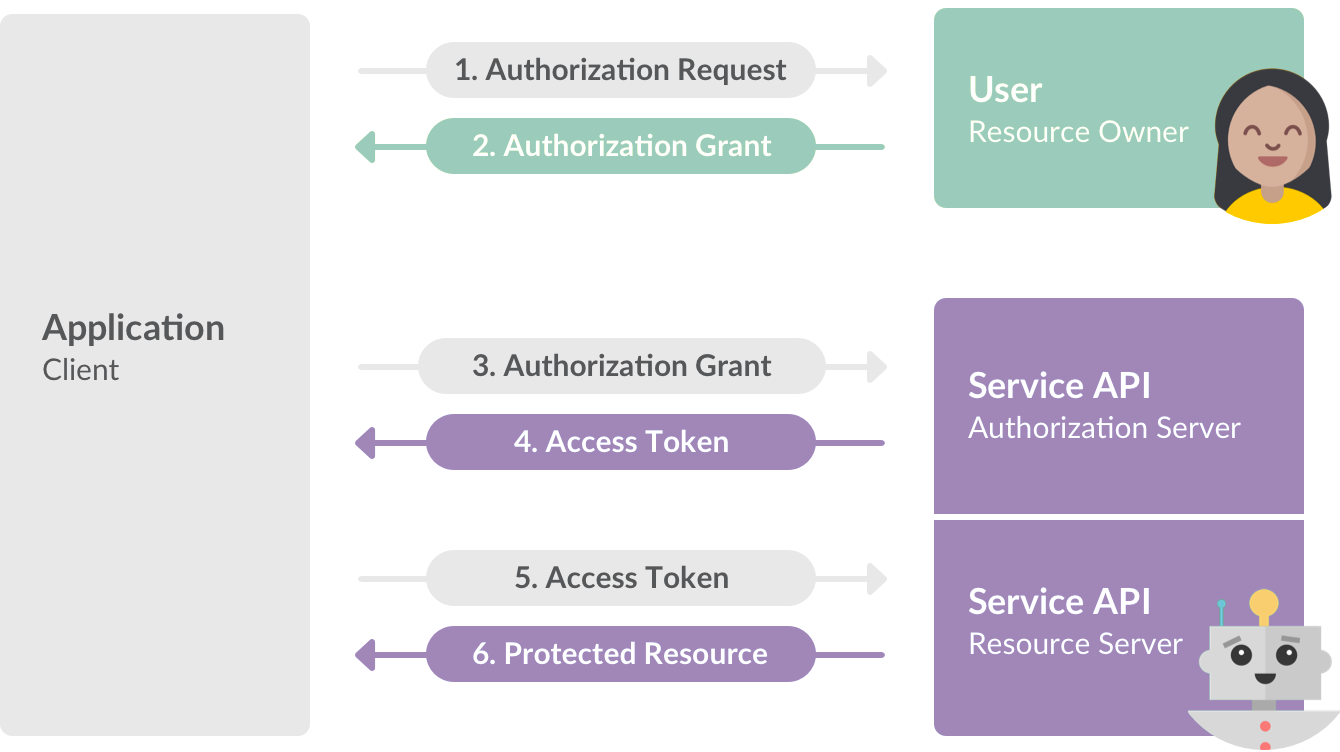
An OAuth 2 style flow used by the Slack API
Responses
It’s important to signal success or failure to clients so that they know what they should do next if anything. Did their request succeed? (2xx) Did it fail permanently? (ie It’ll never succeed because it was invalid 4xx) Did it fail temporarily and they should try again? (ie Service not available, or a bug was found 5xx)
Links
- How we design our APIs at slack
- Do one thing well. What they’re getting at here is a single kind of resource should be focused / limited in what it returns to an apiclient. A mish-mash of many different concepts eventually bloats a response making it unwieldy to use and transfer across the wire
- Invest in developer tools and documentation. How quickly can a new apiuser set up a Hello, world type example?
- Consistency across api endpoints is important. Make sure naming conventions are followed. (First you should have some :))
- Returning meaningful errors to an apiclient will only help them spot and fix bugs sooner. I have been bitten by crappy errors returned by 3rd party APIs very much in the last couple of years
- Include pagination options where it makes sense up front
- Set limits! Rate and the number of resources that are return in a single request
- Try to avoid breaking changes
- Design Best Practices for REST Apis: Good tips I think
- Know basic http stuff
- verbs - get READ, put UPDATE, post CREATE, patch SELECTIVE UPDATE, delete DELETE
- return codes (1xx info? Never really used these myself, 2xx ok, 3xx redirect, 4xx client error, 5xx server error)
- url construction (eg /books/)
- Structured response, preferably json (include Content-Type header -> application/json)
- Pluralization for resources
- Don’t stack them eg not great -> /authors/rjordan/books, better -> /books?author=rjordan (You know exactly what kind of thing you’re asking for and filtering based on a trait of said thing)
- Return errors in the response body (With reasonable structure)
- Use status codes reasonably, consistently
- 401 == 1 not authenticated (Unauthorized), 403 == not authorized (forbidden)
- Know basic http stuff
- The 5 Most Important HTTP Headers: Headers important to backend servers intended for api use or just serving resources over http generally
- Accept eg text/html, application/xhtml+xml
- Content-Type eg application/json
- Authorization eg Authorization: Bearer
, Authorization: Basic - Cookie / Set-Cookie
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin


